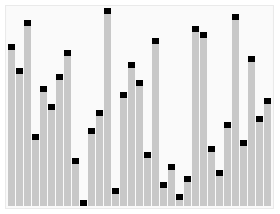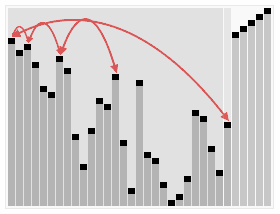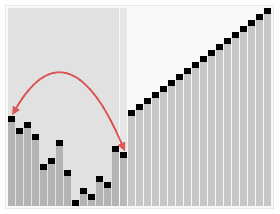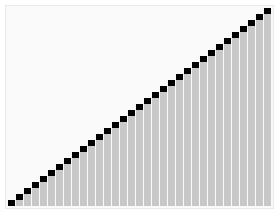
Write a C# Sharp program to sort a list of elements using Heap sort ?
- برمجة سي شارب
- برمجة
- 2021-05-29
- ahmadghneem
الأجوبة
using System;
namespace Heap_sort
{
public class MainClass
{
public static void Main (string[] args)
{
int[] mykeys = new int[] {2, 5, -4, 11, 0, 18, 22, 67, 51, 6};
//double[] mykeys = new double[] {2.22, 0.5, 2.7, -1.0, 11.2};
//string[] mykeys = new string[] {"Red", "White", "Black", "Green", "Orange"};
Console.WriteLine("\nOriginal Array Elements :");
printArray (mykeys);
heapSort (mykeys);
Console.WriteLine("\n\nSorted Array Elements :");
printArray (mykeys);
Console.WriteLine("\n");
}
private static void heapSort<T> (T[] array) where T : IComparable<T>
{
int heapSize = array.Length;
buildMaxHeap (array);
for (int i = heapSize-1; i >= 1; i--)
{
swap (array, i, 0);
heapSize--;
sink (array, heapSize, 0);
}
}
private static void buildMaxHeap<T> (T[] array) where T : IComparable<T>
{
int heapSize = array.Length;
for (int i = (heapSize/2) - 1; i >= 0; i--)
{
sink (array, heapSize, i);
}
}
private static void sink<T> (T[] array, int heapSize, int toSinkPos) where T : IComparable<T>
{
if (getLeftKidPos (toSinkPos) >= heapSize)
{
// No left kid => no kid at all
return;
}
int largestKidPos;
bool leftIsLargest;
if (getRightKidPos (toSinkPos) >= heapSize || array [getRightKidPos (toSinkPos)].CompareTo (array [getLeftKidPos (toSinkPos)]) < 0)
{
largestKidPos = getLeftKidPos (toSinkPos);
leftIsLargest = true;
} else
{
largestKidPos = getRightKidPos (toSinkPos);
leftIsLargest = false;
}
if (array [largestKidPos].CompareTo (array [toSinkPos]) > 0)
{
swap (array, toSinkPos, largestKidPos);
if (leftIsLargest)
{
sink (array, heapSize, getLeftKidPos (toSinkPos));
} else
{
sink (array, heapSize, getRightKidPos (toSinkPos));
}
}
}
private static void swap<T> (T[] array, int pos0, int pos1)
{
T tmpVal = array [pos0];
array [pos0] = array [pos1];
array [pos1] = tmpVal;
}
private static int getLeftKidPos (int parentPos)
{
return (2 * (parentPos + 1)) - 1;
}
private static int getRightKidPos (int parentPos)
{
return 2 * (parentPos + 1);
}
private static void printArray<T> (T[] array)
{
foreach (T t in array)
{
Console.Write(' '+t.ToString()+' ');
}
}
}
}
أسئلة مشابهة
القوائم الدراسية التي ينتمي لها السؤال